7.3. Comparisons based on data from two processes
7.3.5. |
Do two arbitrary processes have the same mean? |
The U-test (as the majority of nonparametric tests) uses the rank sums of the two samples.
- Rank all (n1 + n2)
observations in ascending order. Ties receive the average
of their observations.
- Calculate the sum of the ranks, call these
Ta and Tb
- Calculate the U statistic,
-
Ua =
n1(n2) +
.5(n1)(n1 + 1) -
Ta
or
-
Ub =
n1(n2) +
.5(n2)(n2 + 1) -
Tb
where Ua + Ub = n1(n2).
-
z = [ U - E(U)] /
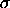
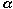 /2
for a two-tailed test or z
at
/2
for a two-tailed test or z
at 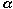 level, for a one-tail test.
level, for a one-tail test.
For small samples use tables, which are readily available in most textbooks on nonparametric statistics.
| Group A | Rank | Group B | Rank |
| .55 | 8 | .49 | 5 |
| .67 | 15.5 | .68 | 17 |
| .43 | 1 | .59 | 9.5 |
| .51 | 6 | .72 | 19 |
| .48 | 3.5 | .67 | 15.5 |
| .60 | 11 | .75 | 20.5 |
| .71 | 18 | .65 | 13.5 |
| .53 | 7 | .77 | 22 |
| .44 | 2 | .62 | 12 |
| .65 | 13.5 | .48 | 3.5 |
| .75 | 20.5 | .59 | 9.5 |
| N | Sum of Ranks | U | Std. Dev of U | Median | |
| A | 11 | 106.000 | 81.000 | 15.229 | 0.540 |
| B | 11 | 147.000 | 40.000 | 15.229 | 0.635 |
Enter value for
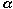 (press Enter for .05): .05
(press Enter for .05): .05
Enter 1 or 2 for One- or Two-sided test: 2
E(U) = 60.500000
The Z-test statistic = 1.346133
The critical value = +/- 1.960395.
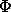 (1.346133)
= 0.910870
(1.346133)
= 0.910870
Right Tail Area = 0.089130
Cannot reject the null hypothesis.
A two-sided confidence interval about U - E(U) is:
DELTA is the absolute difference between U and E(U).
The test statistic is given by: (DELTA / SIGMA).

